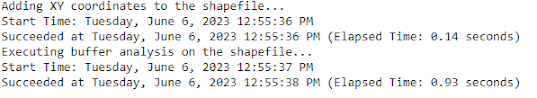
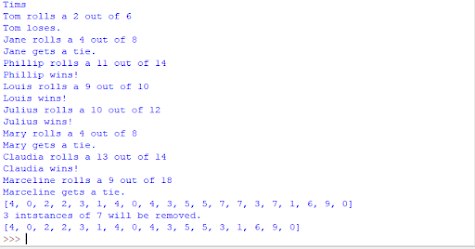
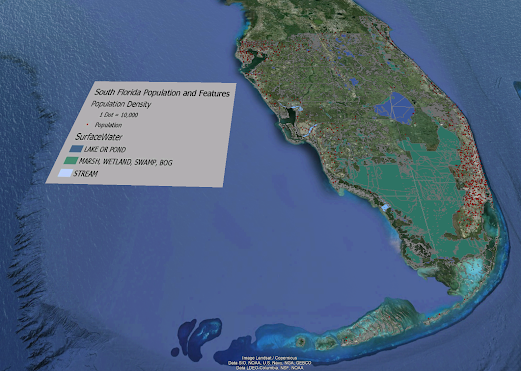
For this weeks lab we used different band combinations to identify different features in Northwest Washington.
The image on the left shows bare soil features on the map, the areas covered in the red/brownish color are the features covered by bare soil. This was found using the TM False Natural Color which uses the band combination of RGB: 5, 4, 3.
The image in the middle shows snow features on the map, the areas covered in the yellow and purple colors indicate areas where snow has fallen or could collect due to elevation. This was found using the band combination of RGB: 2, 4, 5.
The image on the right shows the urban features on the map, the areas covered in grey color are features covered by urban features/development. This was found using the TM False Color IR band combination of RGB: 4, 3, 2.